The Internet
The internet, how it works, who created it and who controls it has been a major question in the heart of many people, a lot of people don’t really understand what the internet is and where it came from. I’m here to help you understand and to explain to you in details how the internet works. So, let’s take a ride.
To start with, we need to know how the internet began, and who controls the internet. In the early 1970s, Vint Cerf and Bob Khan were working on the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET), a project for the US Defence Department whose goal was a computer network that was decentralized so the government could access and distribute information in the case of catastrophic event. The internet was an accidental result of the ARPANET project. The internet is independently operated and no one controls it as it is a decentralized network.
PROTOCOL
Now let’s talk about what a protocol, packet and router is. A Protocol is a standard set of rules that allows electronic devices (like computers) to communicate with each other over a network. These rules include; types of data transmitted, commands used to send and receive data, and how data transfers are confirmed. All data of protocols are stored in binary information. Protocol language is a mixture of bits, characters, integers etc. There are different protocols used on the internet, we will discuss some of them below;
- Transmission control protocol (TCP) / Internet protocol (IP)
- Domain Name System (DNS)
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (IP)
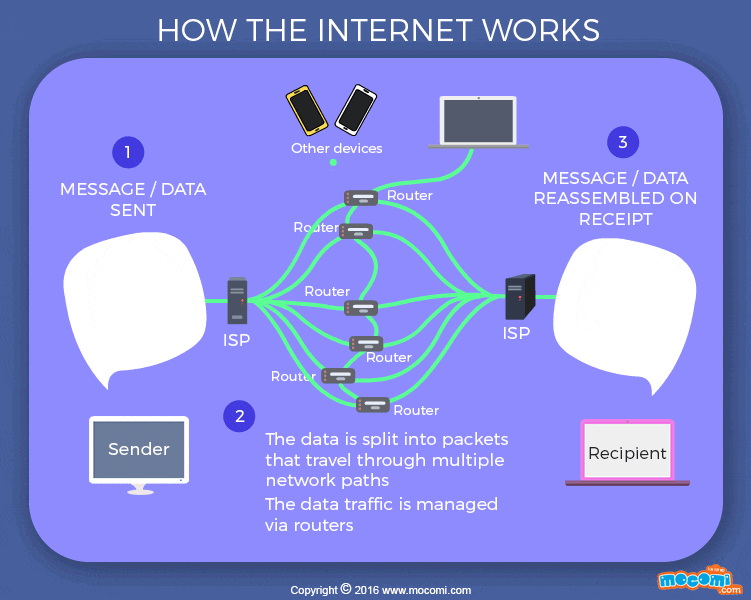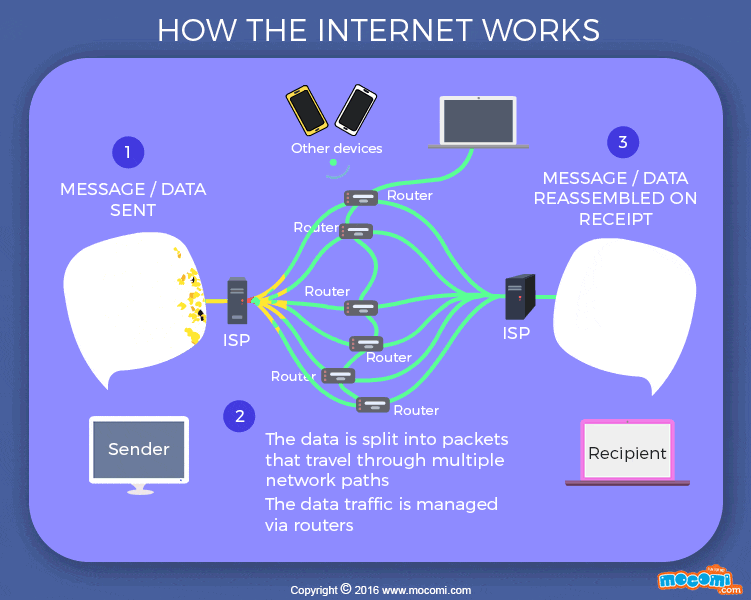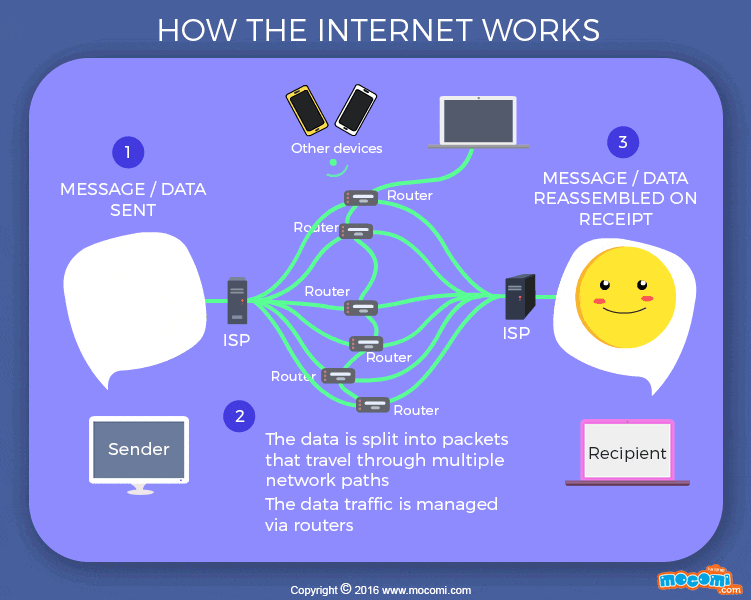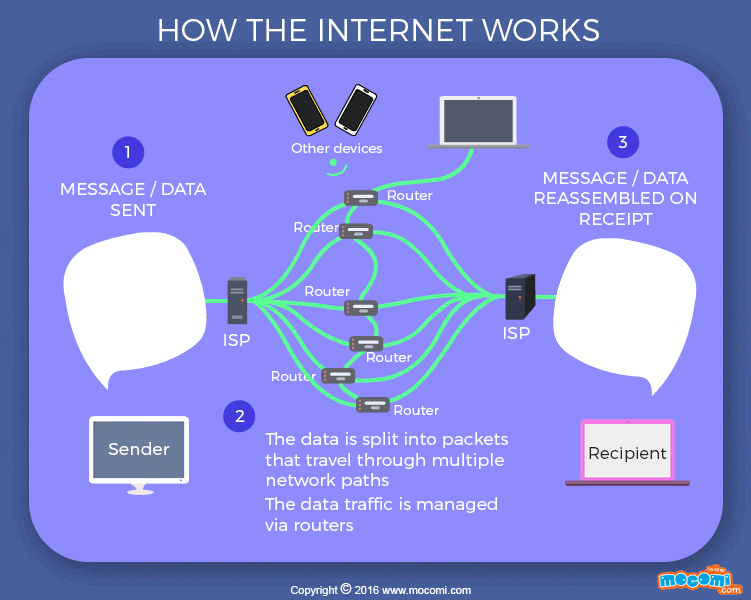
Transmission control protocol (TCP) is a collection of standards that allows systems to communicate over the internet. It creates and maintain connection between hosts. The Internet Protocol (IP) provides a standard set of rules for sending and receiving data over the internet, it specifies how the address is attached to the packet. A packet is a fragment of message (data) sent across the internet in a less direct fashion. The maximum packet size has about 1,000 to 3,000 characters. Each packets have the IP address of where it came from and where it’s going to. These packets can be moved through routers from a source computer to a destination computer smoothly through a process called packet routing network. A command line-tool, traceroute is used to see how packets moves (hop) from one router to another. TCP and routers are scalable; more routers, more reliable the internet becomes.
The IP doesn’t guarantee safe delivery of packets to their destination, most especially when a router receives more packet than it can process. Then there will be packet loss. However, TCP ensures that packets that are loss are re-transmitted by having the destination computer communicate with the source computer in case of packet loss.
Just like your house address has country, city, street and house number, IP address is also organized in hierarchy, each of the number of your computer IP address is represented in bit. The traditional IP address is 32-bits long and 8-bits for each part of the address.
The address of the internet is called IP address and it has two standards;
• IPv4 (for example 212.78.1.25), it supports 2³² (about 4 billion) possible unique addresses, and it is no longer enough for every user of the internet. Therefore, there is need for an IP address that can accommodate more users, which is IPv6 with a longer IP address.
• IPv6 (for example 3ffe:1893:3452:4:345:f345:f345:42fc) supports 2¹²⁸ possible unique addresses, which covers about 340 undecillion unique addresses that can never be exhausted.
For a router to know where to send a packets, it doesn’t need to know every IP address, it only need to know the outbound link. IP addresses can be broken into;
- Network Prefix: 129.42
- Host Identifier: 13:69
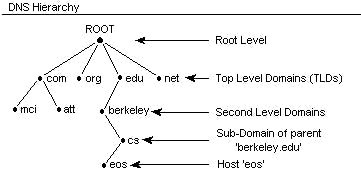
Networked computers resolved or locate IP addresses through the Domain Name System (DNS), a decentralized database of mapping from domain names to IP addresses.
Domain Name System (DNS)
The computer uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to look up the domain name to get the associated IP address which is used to connect your computer to the destination on the internet.
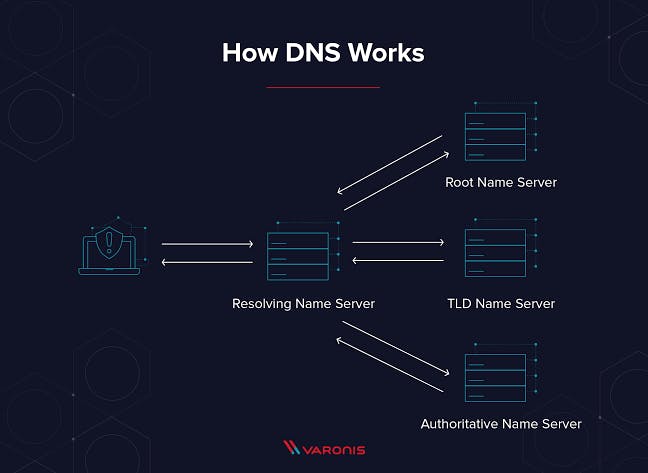
One DNS server cannot handle billions of user’s request, DNS servers are connected in a distributed hierarchy. The responsibilities are distributed between major domain such as .org, .com, .gov, .net etc.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the language used to communicate between web browsers and servers, it uses cookie that a website used to remember who you are. It is an application-layer protocol that is used for transferring files on the internet. Secured Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security are layers of security around your communication to protect them from tamper, they provide lock next to your https:// on your browser. HTTPS protocol ensures that your HTTP request is secured and protected. HTTP and DNS manage the sending and receiving of web files.

ENCRYPTION AND DECRYPTION
Let’s talk about how safe your data and personal profile is on the internet. You may be wondering whether your information on the internet is safe as it said that it is an open network, yes, your information is safe on the internet.
The internet is an open-public system. While on the internet, a message is encrypted from the sender and decrypted when it gets to the receiver. Encryption is the changing or scrambling of a message to hide the original text while Decryption is the process of unscrambling the message to make it readable. Nowadays, secured communications are encrypted using 256-bits keys. Symmetric Encryption is when the sender and receiver share the same key to encrypt and decrypt information. Since the internet is an open-public system, it uses Asymmetric encryption; a public key for encrypting and decrypting information (a public key that can be exchanged with a private key).
To securely transmit a sensitive data like credit card over the internet, the solution to this is encryption and authentication through SSL/TLS. SSL stands for Secured Sockets Layer, developed by Netscape in 1994 but a later more secure version was devised and renamed TLS, which stands for Transport Layer Security; it allows secure internet communication of sensitive information through encryption and authentication.
Encryption allows all messages between client and server to be encrypted by Transmission Control Protocol connection before breaking it into packet, while Authentication means that the client can trust that the server is who it claims to be.
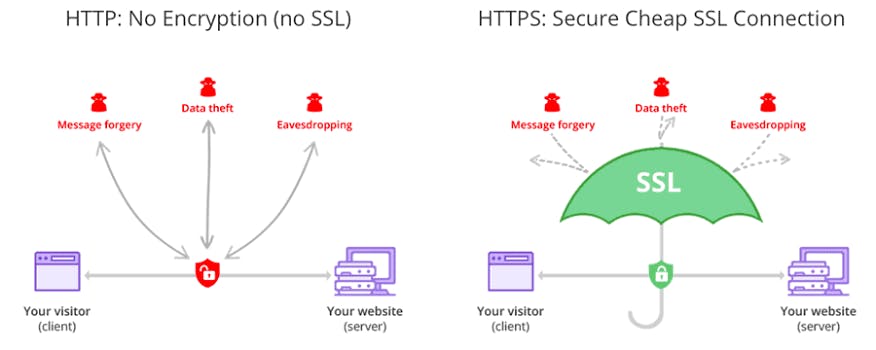
However, if a hacker intercepts an SSL-encrypted session, the hacker encounters a temporary secret key encrypted for the client by the server, and because the hacker doesn’t have the private key, it can’t decrypt any of the messages between the client and the server.
WIRE, CABLE AND WIFI
You may be wondering that by which medium information is moved from one place to another, does it have anything to do with wires and cables or wifi. The internet shares binary information made of bits (binary codes), which is the atom of information. Nowadays, bit is sent by light, electricity and radio waves. The Bandwidth Maximum Transmission (BMT) capacity of a device helps to send message faster than light and electricity, and it is measured in bit rate. Bit rate is the number of bits that we can send over a given period of time usually measured in seconds. The electricity is cheap, but sometimes there may be network loss. The light is super-fast and can be connected with your Ethernet wire (a fiber optic cable). A beam of light is sent through the cable and it bounce at various angle of the wire. Other signals can be sent bouncing at different angle of the cable without any interruption, all of them travelling at the speed of light, you can go many miles without signal loss, but it is expensive and hard to maintain. Finally, the BMT uses radio signals to send bits from one place to another, converted from binary to radio waves at different frequencies. The receiving machine reverse the process and converts it back to binary code on your computer. It only works in short range, that is why wireless internet relies on the wired internet.
Thank you for reading.